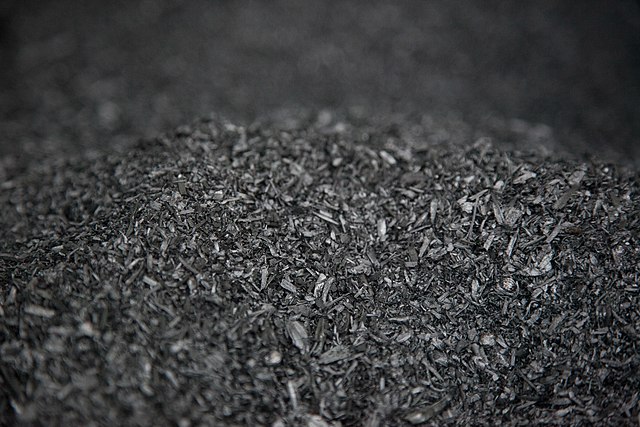
The biochar market has been experiencing significant growth in recent years. This phenomenon can be attributed to various factors that intertwine environmental sustainability, agricultural efficiency, and emerging technologies. Biochar, a carbon-rich product derived from the pyrolysis of biomass, has garnered attention as a potential solution for climate change, soil enhancement, and waste management. Understanding the size, trends, projections, and opportunities within this flourishing market reveals a complex landscape that is ripe for exploration.
To comprehend the biochar market’s magnitude, we must first examine its current state. As of the latest analyses, the biochar market is estimated to be worth several hundred million dollars, with projections indicating expansion that could see it reach over a billion dollars within a decade. This burgeoning interest stems from increasing recognition of biochar’s multifaceted applications and benefits, ranging from carbon sequestration to improved soil fertility. Furthermore, as governments and organizations heighten their commitment to sustainable practices, the demand for biochar is poised to escalate exponentially.
One pivotal trend fueling the biochar market’s growth is the global shift toward sustainable agriculture. Traditional farming methods often lead to soil degradation, reduction in fertility, and increased greenhouse gas emissions. Biochar, acting as a soil amendment, enhances soil structure, boosts nutrient retention, and fosters healthier microbial ecosystems. As farmers and agronomists seek innovative strategies to counteract the adverse effects of climate change on agriculture, biochar presents a compelling solution. Notably, its ability to improve crop yields while simultaneously sequestering carbon makes it an attractive option in a highly competitive agricultural landscape.
In addition to agricultural applications, biochar is gaining traction in the context of waste management. The escalating generation of organic waste poses significant challenges for municipalities and industries alike. Biochar production utilizes waste material—such as crop residues, forestry by-products, and municipal solid waste—effectively converting it into a valuable resource while minimizing landfill contributions. This dual benefit of waste reduction and resource recovery accentuates the biochar market’s role as a component of the circular economy, further enticing stakeholders to invest in its development and commercialization.
Another significant trend influencing the biochar market is the enhancement of technologies associated with its production. Continuous advancements in pyrolysis techniques and carbon capture methodologies are refining the efficiency and scalability of biochar production processes. Emerging technologies, like slow-pyrolysis and hydrothermal carbonization, are garnering attention for their ability to produce biochar with enhanced properties tailored for specific applications. These innovations are not only augmenting production rates but also generating high-quality biochar that meets the growing demands of discerning markets, thereby catalyzing new avenues of opportunity.
Moreover, the regulatory landscape is shifting in favor of biochar utilization. Governments and international organizations increasingly recognize the role of biochar in achieving climate goals. Incentives and subsidies for biochar production, alongside stringent emissions targets, create a favorable environment for stakeholders eager to integrate biochar into broader sustainability strategies. This supportive regulatory framework not only cultivates market stability but also drives investments into research and development, enhancing the quality, application, and adoption of biochar across various sectors.
Another opportunity arises from the biochar market’s intersection with carbon credits. As businesses and industries increasingly strive to reduce their carbon footprints, biochar production presents a viable avenue for generating carbon credits. The ability of biochar to sequester carbon for extended periods allows producers to qualify for carbon trading programs. This integration establishes a financial incentive that could dramatically alter the economic calculus surrounding biochar production, encouraging further investment and innovation within the sector.
Investment in biochar research is witnessing an upward trajectory, driven by academic institutions, private enterprises, and government entities. As the understanding of biochar’s varied benefits continues to evolve, research initiatives are delving into customized formulations suited for distinct crops and environmental conditions. Collaboration across sectors fosters a dynamic ecosystem where knowledge exchange accelerates advancements in biochar technology. The quest for performance optimization, including parameters such as surface area and molecular structure, illustrates the depth of inquiry currently underway.
Despite the promising trends and opportunities within the biochar market, certain challenges exist that warrant consideration. The production costs associated with biochar need to be reduced for widespread adoption. Additionally, public awareness and understanding of biochar must be improved for consumers to fully embrace its benefits. Education campaigns aimed at elucidating the advantages of biochar, accompanied by demonstrative success stories, will be vital in fostering a robust market environment.
The global biochar market embodies a confluence of sustainability, innovation, and opportunity. With its diverse applications spanning agriculture, waste management, and carbon sequestration, biochar stands at the forefront of environmental solutions for the future. As investment flows into research and development, and as the regulatory framework supports its adoption, the market is poised not only for growth but for transformational impact. In navigating the complexities of the biochar landscape, stakeholders can capitalize on opportunities that align with the broader goals of sustainability and resource efficiency, ensuring a resilient and thriving biosphere for generations to come.