The Amazon rainforest, often revered as the lungs of our planet, harbors secrets that whisper of ancient civilizations and a sustainable relationship with the earth. At the very heart of this verdant expanse lies Terra Preta de Índio, or “Indian Dark Earth”—a fertile enigma whose allure captivates both scientists and environmentalists alike. Much like the carefully organized chaos of a symphony, this dark earth encapsulates the delicate interplay between nature and humanity, revealing a story that transcends time and borders.
Terra Preta is not merely soil; it is a living testament to human ingenuity and ecological harmony. Formed through centuries of deliberate practices by Indigenous peoples, it is a remarkable amalgamation of charred organic material, compostable nutrients, and microbial life, creating an ecosystem brimming with fertility. But how did this extraordinary substance emerge in an environment where traditional soil often falters?
The Genesis of Terra Preta
Centuries prior to the arrival of Europeans, early inhabitants of the Amazon region developed methods to combat nutrient-poor sedimentary soils. They ingeniously created Terra Preta, a fertile black earth, believed to have been born from a combination of slash-and-burn agriculture and meticulous waste management, including food scraps, bones, and the intentional burning of biomass. It is akin to a culinary masterpiece where various ingredients unite to create a sumptuous dish; each component’s unique contribution enhances the final product’s richness.
At a glance, Terra Preta distinguishes itself from the surrounding, nutrient-deficient soils, which tend to be acidic and incapable of sustaining high-yield agriculture. This stark contrast invites curiosity: How can a landscape so lush harbor soils so impoverished, and what secrets lie hidden within the depths of the Amazon’s dark heart?
The Science Behind the Magic
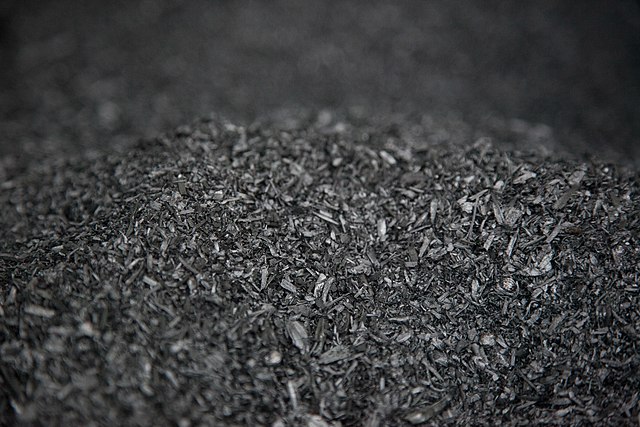
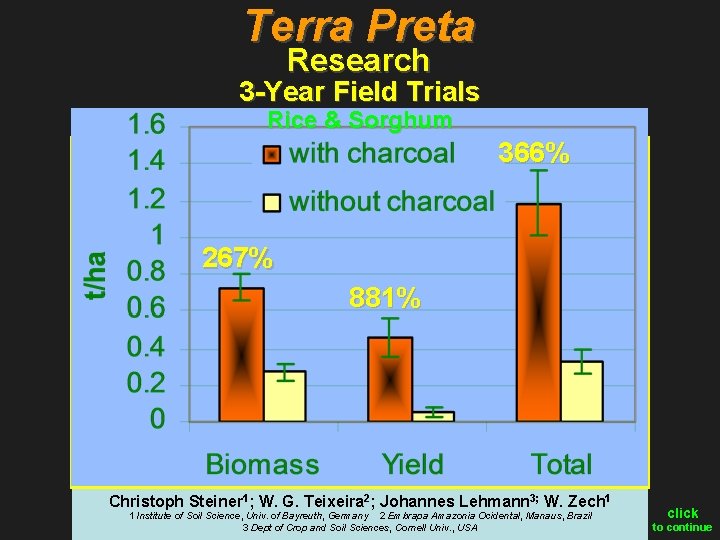
The appeal of Terra Preta is rooted in its distinctive composition. Comprised of charcoal, organic matter, pottery shards, and microbial communities, it serves as a testament to sustainable agricultural practices. The charcoal, or biochar, is particularly significant. Often described as a time capsule, it has the incredible capability of sequestering carbon, thus playing a dual role in enhancing soil fertility while mitigating climate change. One can liken charcoal in Terra Preta to a sponge, soaking up critical nutrients and moisture, rendering them available to plants.
In addition to its remarkable characteristics, Terra Preta is teeming with microorganisms that establish symbiotic relationships with plants, facilitating nutrient absorption. This vibrant web of life underscores an invaluable lesson: productivity can flourish through cooperation, resonating with the interconnectedness of ecosystems. The delicate balance achieved in Terra Preta speaks to the mastery of ancient agrarian techniques, which continue to resonate in contemporary discourse on sustainable agriculture.
The Societal Impact
Historically, the benefits of Terra Preta extended beyond the soil itself. It was a cornerstone of the agricultural practices of pre-Columbian societies, facilitating the cultivation of staple crops such as maize, cassava, and beans. This intricate web of life not only supported dietary needs but also nurtured social structures and cultural identities. The legacy of these Indigenous practices continues to inspire modern agricultural paradigms, anchoring them in the ethos of sustainability.
The advent of globalization, however, has ushered in an era fraught with challenges. The migration of populations and expansive agricultural practices threaten to dismantle the intricate tapestry woven by Indigenous wisdom. Yet, as society grapples with environmental degradation, the allure of Terra Preta calls out to us, reminding us of the potential for regeneration and revitalization through respect for our natural world.
Modern Implications and Sustainable Practices
As the specter of climate change looms large, modern agriculture increasingly turns its gaze toward Terra Preta. Researchers and farmers alike are exploring the potential for creating artificial versions of this dark earth, thereby integrating its principles into contemporary farming practices. The quest for solutions is reminiscent of alchemy—a search for turning the leaden weight of modern challenges into the gold of sustainable solutions.
Moreover, the adoption of biochar has gained traction, heralding a move toward ecological consciousness in agriculture. As practitioners rediscover the versatility of biomass, the possibility of creating rich, productive soil from waste emerges as an exciting avenue. This method not only curtails carbon emissions but regenerates ecosystems, allowing nature to reclaim its rightful place.
A Cultural Renaissance
The allure of Terra Preta extends beyond its agricultural ramifications; it evokes a sense of responsibility toward environmental stewardship. Efforts to preserve Indigenous knowledge are gaining momentum, as cultural heritage increasingly intertwines with ecological empowerment. Just as art serves to capture the essence of humanity, Terra Preta invites us to honor the legacy of those who came before by fostering a sustainable future.
The stories enshrined in the black soil resonate like whispered echoes of a time when our relationship with the earth was intimate and respectful. As we forge ahead, Terra Preta stands as a beacon of hope, a narrative woven with threads of wisdom, resilience, and interconnectedness. Embracing the mysteries of the Amazon’s dark earth offers not just insights into agricultural practices, but a profound reminder of the enduring bond between humans and the natural world.
In conclusion, Terra Preta de Índio embodies the complexity of life’s interwoven narratives. It challenges us to rethink our approach to agriculture, sustainability, and our responsibility toward the planet. As we peel back the layers of this extraordinary earth, we unearth not merely a story of soil, but a rich tapestry that connects us all—a reminder that the wisdom of the past can illuminate pathways for the future.